In the first part of our ‘Enterprise SEO Competitor Analysis’ blog post series, you learned why SEO Competitor Analysis is needed and how to get started as we explored the fundamentals of enterprise SEO and how it differs from traditional SEO. We also discussed why understanding your competitors is critical to stand out in the highly competitive search landscape. Together, we covered how to find the top competitors for your next enterprise clients through a 9-step checklist.
In short, our goal was to prepare you to conduct the competitor SEO analysis practically, as identifying your competitors is only the tip of the iceberg. To outperform them in Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), you need to understand what strategies make their SEO campaigns successful.
You need to analyze their top-performing keywords, most popular content, backlinks from relevant referring domains, website structure, mobile friendliness, etc. You have to find the gaps in their SEO strategies so you can add value and provide better results.
The second part of this series is content SEO focused, and here, you will learn how to conduct content analysis and on-page SEO audits in detail with practical examples. I will show you how to carry out keyword gap analysis, backlink gap analysis, and top content analysis practically on your competitors’ websites. At the end, there will be a bonus section named ‘Local SEO’ where you will find the top factors to consider while performing a local SEO audit. To sum up, the topics we will cover in this blog post are:
- How to find a list of less competitive keywords that your competitors’ website is ranked for but not your website.
- How to run a competitor’s backlink analysis to reveal the referring domains from where your competitors’ websites have received backlinks, but not your website
- How to find a list of competitors’ most popular content
- What to check when carrying out an on-page SEO analysis on your competitors’ websites
- 7 must-check factors while running a local SEO competitor
3 Steps Competitor’s SEO Content Analysis Guideline: From Keyword research to top-performing content
Following the first installment of this ‘Enterprise SEO Competitor Analysis’ blog post series, you should now have a list of direct and indirect competitors for your business, products, or services. It is time to focus on the content SEO part. We have prepared a three-step competitors’ content SEO analysis guideline for you. The steps are competitor keyword gap research, competitor backlink gap analysis, and analyzing competitors’ top-performing content.
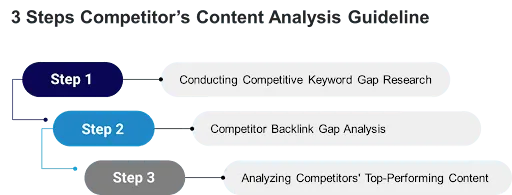
Conducting Competitive Keyword Gap Research
Content is king, but effective keyword research is the ultimate weapon the king will need to win the SEO battle. Therefore, it is safe to say that you may produce high-quality content but not rank high in the SERPs if you do not carry out the necessary keyword gap research. Google has lately been trying to shift the focus from long-tail keywords to understanding the context of the content, also known as semantic SEO. This does not make keyword research less important. You just need to find the right balance and stay away from overuse. If you are curious and want to learn more about semantic SEO, read our latest blog post on semantic SEO here.
Now, let’s return to the point. We want to execute comprehensive keyword gap research, focusing on our competitors’ websites. We especially want to reveal the keywords our competitors are ranked for, but not us. Traditional keyword research techniques will not help us in this case.
Let’s do the analysis on Digital Loop: we are a Munich-based consultancy that offers, among others, SEO as a service. Therefore, we will do the competitor analysis for SEO and select three other companies as a competitor that also offers similar services in Munich. So, the competitors we have chosen are:
| Suxeedo | SEO Agentur | Rankeffect |
Now, let’s begin with the fun part. We will use the ‘Competitive Analysis’ feature from Ahrefs. We will not consider the competitor’s root domains. Instead, we will only analyze their SEO service pages. The ‘Competitive Analysis’ section in Ahrefs should look like this.
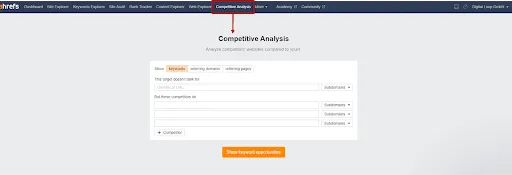
The next step is pretty simple. You should find two options: your target website that does not rank for a set of keywords, and your competitors who actually do. Put your website’s URL in the first option and competitors’ URLs in the second option. You can put up to 10 competitors’ URLs there. Here is an example of how it should look:
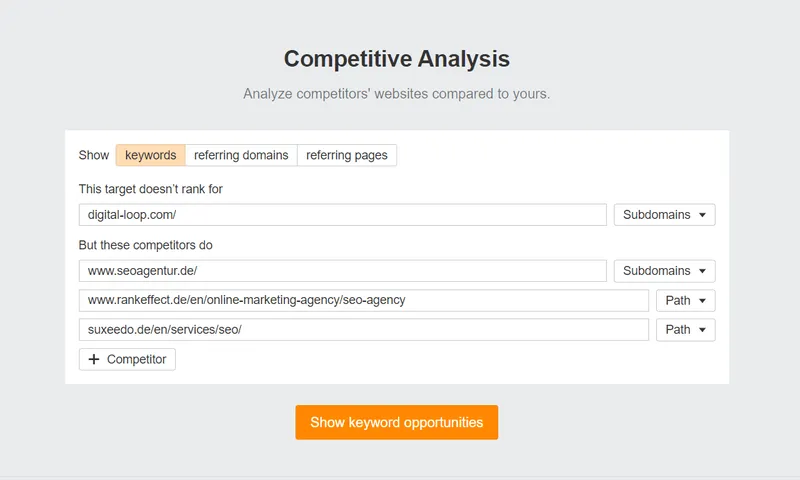
Now click on the ‘show keyword opportunities’ button, and boom! Ahrefs will show you a list of keywords you are not ranked for, but your competitors are. Our simple analysis found 213 relevant keywords where our competitors are ranked, but we are not. You can check the result of the analysis we conducted for the ‘SEO service’ below.
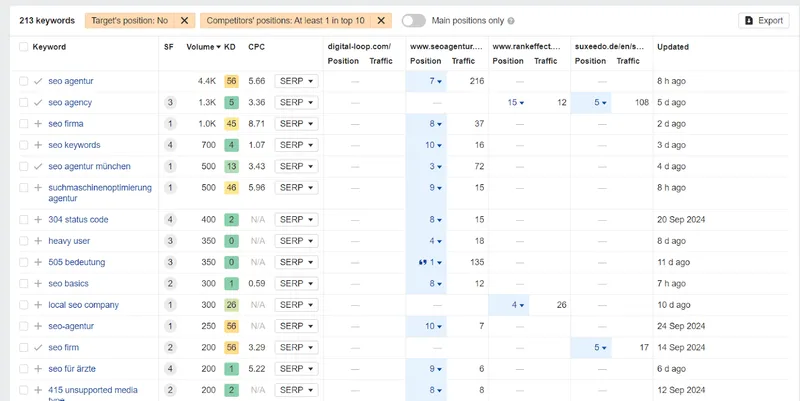
The next crucial step is to export your list of keywords and identify those with the highest potential. Specifically, keywords that have higher search volumes and lower competition. As you go through this process, you’ll likely come across branded keywords specific to your competitors. Make sure to remove these branded keywords, as they won’t help you rank in SERPs. Besides, they do not represent your brand.
User’s Search Intent
While conducting keyword research, you also need to consider the user’s search intent. Search intent is the ultimate goal the visitor wants to accomplish from this visit, such as getting some specific information, finding a website address, comparing different products or services, or buying the products or services.
As Google is trying to establish user experience as one of the core ranking factors, understanding users’ goals and creating content according to those is the key to success. Keywords can be classified into four categories based on the user’s search intent:
- Informational Keywords: Keywords where the intent is to gather information (e.g., ‘how to,’ ‘what is,’ ‘best ways to’).
- Navigational Keywords: Keywords where the intent is to find a specific website or page (e.g., ‘Digital Loop login,’ ‘Digital Loop website,’ ‘Digital Loop careers page’).
- Transactional Keywords: Keywords where the intent is to make a purchase or complete a transaction (e.g., ‘buy,’ ‘order,’ ‘subscribe’).
- Commercial Investigation Keywords: Keywords where the intent is to compare products or services before making a purchase (e.g., ‘SEO vs. SMM,’ ‘Best SEO companies in Munich’).
Competitor Backlink Gap Analysis
High-quality backlinks from relevant niches can help you build higher authority for your topic. Of course, you will still need excellent content and in-depth keyword research. Backlinks from relevant niches work more like a recommendation and directly impact your website’s EEAT score. As a result, Google will rank that page higher in the SERPs and show it more often for queries. By the way, EEAT stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Check out our blog post on EEAT to learn more.
Now, we know that backlinks are one of the most significant ranking factors in SEO. Analyzing your competitors’ backlink profiles can help you understand where their authority comes from and identify link-building opportunities for your own website. It is a common SEO practice to investigate and leverage high-quality referring domains from competitors’ websites and skip spammy and irrelevant referring domains. The question is, how can you audit your competitors’ backlink profiles and find the gap?
You can use Ahrefs for more than just competitors’ keyword research tasks. It is also a powerful tool for exploring your competitors’ backlink profiles. Instead of focusing on keywords, you simply now have to enter your competitors’ domain URLs and head over to the Referring Domains section. This will give you a list of websites linking back to their domains, revealing the sources that are boosting their authority and SEO rankings.
By analyzing your competitors’ backlink strategies, you can identify valuable linking opportunities and potential gaps for your website. With the same competitors you have already been studying, this method provides an even deeper look into how they build their SEO success! The analysis input should look like the image below, as we have used the same competitors:
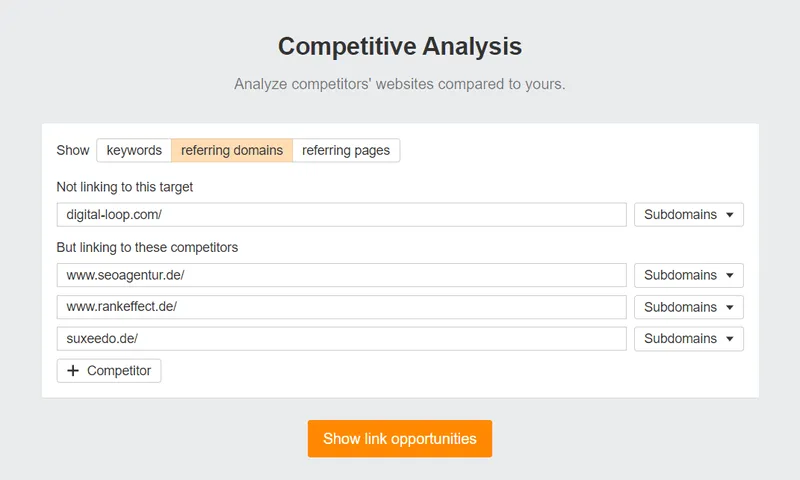
Now, when you click on the ‘Show link opportunities’ button, you should get a list of referring domains from which your competitors’ websites have received links but not yours. Here is a simple example of how the output may look:
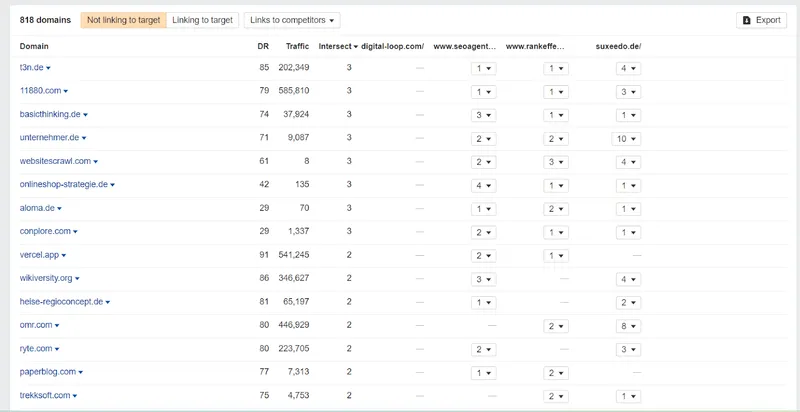
Now, you can create a list of the top relevant referring domains and delete or hide backlinks from irrelevant or spammy referring domains in your Excel or CSV file. Boom! Now, you have a list of high-quality, relevant referring domains that you can use to build high-quality links for your website.
Analyzing Competitors’ Top-Performing Content
You can find what types of content work for your products or services by analyzing your competitors’ content. For example, if your competitors are climbing the ranks and driving tons of traffic with lengthy blog posts, it’s a clear sign that you might need to do the same. Search engines love in-depth, comprehensive content, and if long-form articles work for your competitors, they’ll likely boost your site, too. By creating detailed, valuable content, you’re not just matching your competitors but also showing the search engine algorithm that your content deserves to be seen, engaged with, and ranked higher!
We will use the SEO Agentur domain as an example to show you practically how to analyze their most performing content/landing pages. Follow the following three steps to find the most popular content for your products or services.
1. Log in to Ahrefs and go to the ‘Site Explorer’ section. Enter your competitor’s root domain ( for example, https://digital-loop.com/) and press Enter.
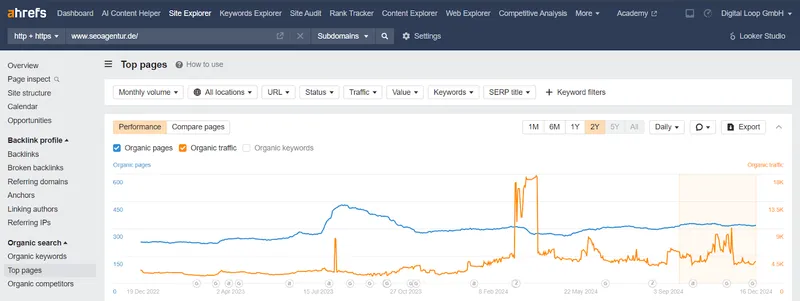
2. Now, scroll down and click on the ‘Top Pages’ from the ‘Organic Search’ section on the left side. Export the top 20-30 results, and cluster them based on content types such as landing pages, blog posts, infographics, or videos.
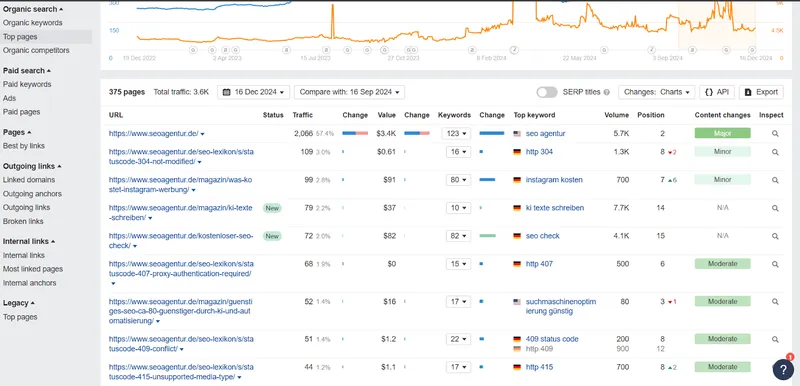
3. The last step will be to draw a pattern and analyze why some pieces of content are doing well and others are not. You should consider some important factors, such as keyword optimization, content length, content quality, number of backlinks, etc.
Separate branded content from the non-branded content
Branded content is promotional or advertorial content that is produced to promote the company or its products or services directly. On the other hand, non-branded content serves a larger purpose and addresses the entire industry.
You would not like to waste time on the branded content since it is specific to your competitors. Check carefully the top-performing non-branded content, whether it is information, commercial, or transactional. Your focus should be on high-ranked commercial or transactional non-branded content since they are adding the most ROI for your competitors.
On-Page SEO Analysis
On-page SEO analysis focuses on the content that is visible to the audience. So, when you analyze the content of your competitor’s websites, you should check different On-Page SEO factors such as meta titles and meta descriptions, internal linking strategy, content structure, readability, and user engagement metrics.
Meta Titles & Descriptions
Meta titles and meta descriptions are not considered ranking factors for SEO by Google, but that does not mean they are not important. Users can not see the meta tags as they are not a part of the content. They are added to help search engine bots crawl and understand your website. Search engines show meta tags in the search results as a landing page preview. Engaging, concise, and actionable meta tags can incite visitors to click and visit particular landing pages or websites. Therefore, meta tags have a strong influence on the click-through rate (CTR) and can increase your traffic if done correctly.
So, when auditing your competitors’ websites, you should carefully check if the meta titles and descriptions are too short or too long. Too-short meta tags do not contain enough information, while too-long meta tags get cut in SERPs. You should also carefully check the quantity of duplicate and missing meta tags.
Internal Linking Strategy
The next step can be to assess how competitors use internal links to distribute authority across pages. If sub-pages are linked to the core topic pages, it becomes easier for search engine bots to find and crawl the pages. On the other hand, pages that are not interlinked to other pages are considered orphan pages. These pages can be left out of indexing because search engine bots may not find them due to a limited crawl budget.
Another benefit of internal linking is that it can help to pass link juice from one page to another. Let’s imagine page A is one of your core landing pages with more than 50 relevant, high-quality external links. Higher external relevant links to a certain page tell search engines that this page is well recognized by other pages. It works more like a reference. You can pass this authority to page C by simply connecting it to page C. Since page A is well recognized by search engines, they will also consider page C to be high-quality content thanks to the interlinking. This is how internal linking can help pass authority:

You can crawl your competitor’s websites using Screaming Frog to inspect their interlinking strategy. You can also use the same tool to discover the total number of orphan pages they have. A higher number of orphan pages indicates that your competitors did not take internal linking seriously.
Content Structure & Readability
Content structure and readability tests should not be skipped while executing a competitor analysis. You should properly inspect whether your competitors use headline tags such as H1, H2, H3, H4, etc. Some rules to follow while implementing H tags include only one H1 tag and no duplicate or missing H2, H3, or H4 tags. There is no limit to the H1 tag word count, but you should try to keep it concise. An ideal approach is to add your focus keyword in the H1. You should carefully look for these issues and keep notes while performing an On-Page SEO audit.
When you write a blog post or landing page content, you should keep the target audience in mind. You would not want your readers to sit with a dictionary while reading your content, right? So, we always suggest writing content that is fun to read and easy to understand for everyone.
You can also dive deep and read your competitor’s content at this stage. If they use too many complex sentences, high-end vocabulary, and long paragraphs, then you can assume their content is less readable. Less readable content can lead to a higher bounce rate, fewer engagements, and limited conversions. So this can also be an opportunity for you to develop more user-friendly content and improve ranking in the SERPs.
User Engagement Metrics
Google rolled out multiple updates in 2024 with the aim of ensuring that only helpful content is at the top of the ranking. I know many of you would not agree that they have been successful. For now, we can agree that they are trying. Producing helpful content will be a more important ranking factor in the upcoming years as the internet is now flooded with GenAI-generated content.
Therefore, Google now prioritizes different user engagement metrics such as bounce rate, click-through rate (CTR), average time on the page, etc. You should manually check whether users are engaged in your competitor’s websites. Then, you should try to find possible reasons and avoid them so that your website stays at the top of the minds of your target audiences.
Bonus Section: Local SEO Competitor Analysis
If you are optimizing a website that focuses on a specific geographic area, you must also carry out a local SEO audit. Whether you or your client is an insurance provider, broker, local restaurant owner, plumber, or boutique store owner, ranking high in local search results is essential for attracting nearby customers.
When you target local visitors, focusing solely on your own website is not enough. In this case, conducting an SEO competitor analysis and understanding the market competition can act as your secret code to succeed in the local market. Here are some factors you should consider while executing a Local SEO Competitor Analysis.
Google My Business (GMB) profile
Check if your competitors’ Google My Business profiles are fully optimized with accurate categories, fresh photos, and up-to-date business hours. If they are not doing these right, it would be a good decision to invest more resources in them.
Target Local Keywords
Do in-depth keyword research and find gaps in your competitors’ use of local keywords (such as “best [product] in [city]”). The next option would be to use these keywords in your meta title, meta description, and H1.
Leverage Local Backlinks
Check which sources your competitors are getting local backlinks from. There is a high probability that you can also manage backlinks from similar sources. Make sure the websites you target are relevant and have good authority. We recommend using Ahrefs to check the site’s authority.
Do not Underestimate Local directories and blogs.
Local directories and blogs can be a good source of traffic and links. Check which directories or local forums your competitors are using. List the popular directories and blogs for a particular area, such as Munich or Frankfurt. You can have a different list for separate products. Now, enlist your business there and publish high-quality content following the guidelines.
Key Takeaways
I hope you have enjoyed reading the second part of this blog post series. I have summed up the key takeaways from this blog post:
- Use tools like Ahrefs to identify keywords competitors rank for that your site doesn’t. Focus on high-volume, low-competition keywords.
- Analyze competitors’ backlink profiles to discover high-quality referring domains and potential link-building opportunities.
- Study the top-performing content of competitors, such as blogs, landing pages, and videos, with the help of Ahrefs’ top page features to identify patterns in keyword usage, content quality, and structure.
- Evaluate different On-Page SEO factors, such as meta titles, meta descriptions, internal linking strategies, and headlines, especially H1 and H2.
- For local SEO audits, make sure you also check Google My Business (GMB) profiles, local keywords, and backlink profiles.
A Little Teaser about Part Three
In this second part of the series, you have learned how to analyze content SEO in detail with practical examples. We have also covered local SEO and mentioned the critical seven factors you should focus on when performing a local SEO audit for your next enterprise projects.
The third and last part of this ‘Enterprise SEO Competitor Analysis’ blog post series will solely focus on technical SEO. Together, we will explore core web vitals (CWV), website speed optimization, website structure, crawlability, and many more. Stay tuned for further updates.
If you have enjoyed reading this blog post, we would like to invite you to explore our other latest posts here. And don’t forget to share this on social media so your friends can also read and implement the strategies we mentioned here.