RAG? Agentic RAG? I know, I know… Many new definitions have appeared lately, but this is our new reality. In just a few years, the evolution of AI has skyrocketed, transforming from simple word recognition into truly powerful systems.
Here’s how this evolution looks:
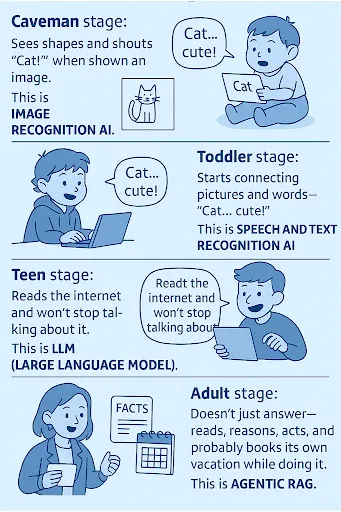
- Caveman stage: Sees shapes and shouts “Cat!” when shown an image. This is Image Recognition AI.
- Toddler stage: Starts connecting pictures and words like “Cat… cute!” This is Speech and Text Recognition AI.
- Teen stage: Reads the internet and won’t stop talking about it. This is LLM (Large Language Model).
- College stage: Learns to double-check facts before bragging. This is RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).
- Adult stage: Doesn’t just answer, but reads, reasons, acts, and probably books its own vacation while doing it. This is Agentic RAG.
This image was generated by AI.
Well, if a few months ago we thought that RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) was the final answer to every problem in AI, today we realize that RAG is only the beginning.
Now, a new idea is emerging: Agentic RAG. This is something new that will change the way we execute purchases on the internet (and not only purchases). Instead of passively retrieving snippets and hoping the model gets it right, an agentic system actually plans, checks (which is important to avoid well-known hallucinations), and acts. It thinks about what it needs, fetches it, verifies it, and even runs small tasks to confirm results.
While traditional RAG is like a helpful librarian handing you documents, Agentic RAG is the researcher who reads those documents, checks the numbers, and drafts a conclusion you can trust.
And the good news? You don’t need a PhD in vector databases to understand the basics of how it works.
From this post, you will learn:
- What Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) actually does (in plain language, without technical clutter, I hope).
- Why Agentic RAG is the next evolution, turning retrieval into reasoning and action.
- How an Agentic RAG loop works step by step: planning, retrieving, reasoning, acting, and verifying.
- I will share with you real-world examples of how enterprises can apply (and are already applying) Agentic RAG in SEO, analytics, and knowledge management.
- You will know the biggest challenges and pitfalls (like context drift, cost, and overengineering traps).
So, fasten your seatbelt and let’s strip away the jargon to see what’s really going on behind this next evolution in AI reasoning.
RAG? Agentic RAG? But… What’s the Difference?
Let’s start with the basics.
Large language models are incredible at generating fluent text, but they have one critical flaw: they don’t “know” anything that wasn’t in their training data. If your organization launched a new product last week or updated its pricing yesterday, the model has no clue.
That’s where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) comes in.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) refers to the approach of providing generative AI models with current knowledge from external data sources.
The idea behind it is simple:
- When you ask a question, the system retrieves the most relevant information from data sources such as websites, documents, databases, or wikis.
- It injects those snippets into the model’s prompt.
- Then the model generates an answer grounded in that fresh, retrieved context.
It’s basically a “fact check before you speak” mechanism for LLMs.
Traditional RAG works in three steps: retrieve, augment, generate. When you ask a question, the system searches through a database or document collection, finds the most relevant text, and feeds those snippets into the model’s prompt. Then the model writes its answer based on that context.
However, as many teams quickly discovered, RAG has limits. It’s a static pipeline. Once the documents are fetched, the model accepts them as truth and writes an answer even if the data is incomplete or contradictory. It doesn’t question the quality of what it retrieved. That’s fine for simple use cases (like answering FAQs), but it fails when tasks require reasoning, cross-checking, or multi-step analysis.
And that’s exactly where Agentic RAG comes in.
Instead of treating retrieval as a one-time step, it turns the process into a loop of reasoning and action. The AI doesn’t just take whatever’s retrieved. It decides what to search, how to interpret it, and what to do next if the information isn’t clear.
Think of it this way:
- Classic RAG is like a librarian who brings you a stack of books based on your question.
- Agentic RAG is a researcher who reads those books, compares the data, runs calculations, and then drafts a well-supported conclusion.
This is a small conceptual step, but one giant leap that transforms AI from a content generator into a decision-making collaborator.
Taking a Closer look: The Agentic RAG Loop (How It Actually Works)
If traditional RAG is a single-lane road where input goes in and an answer comes out, Agentic RAG is a looping highway system with several exits and checkpoints.
The model doesn’t just grab information and respond. It runs a small cycle of reasoning steps before it even begins to write.
Speaking of its logic, at a high level, the Agentic RAG loop follows five phases:
1. Plan: At this first step, the agent decides what it needs to know.
Instead of relying entirely on your prompt, it breaks the question into sub-goals.
Example: If you ask, “Why did our Core Web Vitals drop last month?”, the agent may plan three subtasks: 1. check PageSpeed data, 2. fetch analytics trends, and 3. look up recent code deployments.
2. Retrieve: The agent searches multiple sources dynamically.
The agent might query your document index, scrape a dashboard, run a SQL query, or perform an internet search. At this step, retrieval becomes adaptive: if one source is incomplete, it tries another. Think of it as a researcher who doesn’t stop at the first Google result.
3. Reason: The agent interprets and connects what it found.
Here’s where “agentic” shines: the AI compares data points, spots contradictions, and estimates confidence levels. If two reports conflict, it flags the inconsistency instead of silently merging them. Technically, this involves iterative prompting and internal scoring, meaning the model evaluates its own intermediate answers before the final synthesis.
4. Act: It takes steps beyond text generation.
The agent might run a calculation, call an external API, or launch another retrieval.
Example: In marketing analytics, the agent can calculate month-over-month traffic deltas using real numbers rather than guessing them from text.
And… the good news: This is why many frameworks now integrate function-calling layers, allowing the agent to verify rather than hallucinate.
5. Verify: It checks the final reasoning chain.
A meta-step where the model re-evaluates whether its evidence supports the answer. Some systems even use self-consistency checks. They run the same question multiple times to see if the conclusions align. When all these phases are connected, the result feels less like “chatbot text” and more like an intelligent collaborator.
For instance:
- Customer Support: Instead of retrieving one FAQ paragraph, the agent gathers multiple relevant policies, verifies dates, and summarizes the most recent terms.
- Enterprise SEO: The agent pulls ranking data from BigQuery, correlates it with crawl logs, and writes a short diagnosis of traffic loss (with linked evidence).
- Research Workflows: In pharma or finance, it retrieves papers or filings, cross-checks numbers, and flags anomalies automatically.

This image was generated by AI.
In short:
Traditional RAG = search + answer.
Agentic RAG = search + reason + act + verify.
Again, it’s the difference between asking a librarian for a book and having a full research team that reads it, debates it, and gives you a confident summary.
Why It Matters (Real-World Benefits)
What hits close to home for me is that the beauty of Agentic RAG isn’t just in the technology, but in what it enables. For the first time, large language models can move beyond static Q&A and start behaving like intelligent collaborators that reason through problems, check their own work, and adapt to new information.
Let’s imagine what that might look like in real life.
What Agentic RAG really fixes
Again, in a classic RAG setup, if your query is ambiguous or the retrieved data is incomplete, the model simply improvises (this is where hallucinations begin).
Agentic RAG fixes that. The AI doesn’t just give up; it plans another move. It can reformulate the question, run another search, or combine results from different databases until it’s confident in the answer.
Agentic RAG doesn’t trust itself
Agentic RAG loops include reasoning and validation steps, meaning the AI doesn’t trust its first draft. It can cross-check multiple sources, detect conflicting facts, and flag uncertainty levels.
This turns AI from a “probabilistic storyteller” into a cautious analyst that actually knows when it doesn’t know.
Agentic RAG replicates Human-Like Decision Flows
The biggest shift is, perhaps, conceptual: Agentic RAG mirrors how humans think.
We don’t memorize every fact; we recall, check, and reason through evidence. That’s what these agentic loops replicate—contextual reasoning on demand.
Example: Imagine an SEO intelligence agent that’s asked why conversions dropped last month. Instead of pulling one dataset and guessing, it automatically checks Google Search Console, fetches page-speed metrics from Lighthouse, compares date ranges in GA4, and only then builds a narrative supported by evidence.
Agentic RAG in Enterprise Contexts (with Examples)
Working with enterprises, we know they sit on oceans of data. They have analytics dashboards, CRM systems, internal wikis, product sheets, policy documents, and campaign archives. They know your mom’s birthday and the date you buy a new laptop.
Yet, most of that information remains unsearchable intelligence (technically stored but practically forgotten).
RAG was supposed to fix that
It made it easier to retrieve what’s relevant, but retrieval alone doesn’t solve the deeper problem. Enterprises don’t just need answers; they need decisions grounded in verified, up-to-date data. That’s where Agentic RAG fits perfectly.
Here’s how enterprises can use Agentic RAG.
Example #1: Agentic RAG can help with campaign optimization.
Everyone knows that classic campaigns are often only monitored after launch and evaluated later.
Now imagine that your marketing AI constantly monitors all relevant key figures and draws on additional information as needed, such as current conversion data, web traffic, or even external signals like news in the market environment. Your Agentic RAG can immediately react like a Marketing Data Analyst based on this data. It can suggest reallocating the budget, targeting particularly active groups more strongly, or adjusting A/B tests when new trends emerge.
Example #2: Agentic RAG can help with business insights.
In large companies, insights are scattered across multiple tools like Google Analytics, Salesforce, Data Studio, and internal SQL databases. An Agentic RAG-powered assistant can autonomously fetch data from each source, cross-reference it, and reason about the outcome.
Ask: “What’s causing our bounce rate to rise on mobile?”
The agent might pull Core Web Vitals data, Lighthouse metrics, and GA sessions, spot a correlation with slower LCP times, and even validate it against release logs.
Example #3: Enterprise SEO and Content Intelligence
For SEO teams, RAG already helps with structured data audits or content retrieval. But with agency, it can diagnose performance shifts on its own.
An Agentic RAG system could, for instance:
- Detect ranking volatility for “travel insurance” queries,
- Check whether those pages were affected by an AI Overview rollout,
- Fetch CWV metrics for those URLs,
- Compare historical patterns,
- And finally summarize:
Your LCP degradation and internal linking changes correlate with visibility drop after the update.
Example #4: Customer Support and Knowledge QA
Enterprise support teams often deal with massive documentation stacks that update frequently.
An Agentic RAG agent doesn’t just retrieve the first matching article; it checks whether the information is current, whether policies have changed, and what exceptions apply. It can even verify accuracy by querying internal APIs for the latest data. The result is faster, contextually precise support that scales without retraining models or manually tagging data.
Example #5: Knowledge Management That Thinks Back
A legal department can ask, “What changed in our GDPR policy between 2022 and 2025?” Instead of dumping two documents, the system runs a diff, flags updated clauses, and cites exact sources. That is a cognitive leap. It is retrieval that reason.
In short, Agentic RAG turns enterprise data ecosystems into living systems that think, check, and act across silos. Instead of asking “what does our data say?”, teams start asking “what does our data mean right now, and what should we do next?”
That’s the difference between automation and intelligence. And it’s where Agentic RAG begins to feel less like a tool and more like a colleague.
Let’s Talk About Challenges
Agentic RAG sounds powerful (and it likely is), but it’s not a silver bullet. Every time you add autonomy, you also add complexity. And complexity always comes with cost, latency, and risk.
Let’s look at where things can (and often do) go wrong.
Challenge #1: Garbage In, Garbage Out (Still Applies)
Based on the title of this chapter, you can probably already guess what I’m talking about.
Well, RAG depends entirely on the quality of your data. If the underlying documents are outdated, inconsistent, or poorly chunked, the system can’t reason its way out of that mess. You’ll simply end up with more confident hallucinations. This means that before experimenting with Agentic RAG, it’s worth investing in proper data hygiene, such as clear structure, metadata tagging, and consistent version control. Reasoning only works when the retrieval layer feeds it truth.
Challenge #2: Context Drift and Over-Looping
One of the biggest issues I’ve seen when testing agentic systems is context drift. The AI gradually shifts away from the original question as it keeps planning, retrieving, and refining.
In long reasoning loops, the model may forget what it was solving and start chasing tangents.
Challenge #3: Latency and Token Costs
Each reasoning step means another API call, another retrieval query, and another prompt expansion. In enterprise-scale deployments, that multiplies fast.
Without optimization, such as caching or reusing embeddings, Agentic RAG pipelines can become slow and expensive, especially when users expect real-time interaction.
Challenge #4: Evaluation Is Hard
In a traditional RAG pipeline, you can measure accuracy through retrieval precision and recall.
But how do you measure the quality of reasoning? Agentic systems often rely on subjective evaluation, such as human review, scoring rubrics, or synthetic QA datasets. This means that until evaluation frameworks mature, building robust feedback loops remains one of the biggest challenges for enterprise adoption.
Challenge #5: Over-Engineering Risk
Not every problem needs an agentic loop. Sometimes, a simple retrieval and answer setup outperforms a complex reasoning chain just because it’s faster and easier to maintain. I’ve seen teams jump straight into multi-agent orchestration before they even had a clean data pipeline.
The smarter move is incremental. Start with RAG, identify failure points, then add reasoning loops only where they add measurable value.
What’s Next? (Multi-Agent RAG Ecosystems)
Agentic RAG is only the first step toward a much larger transformation, a world where AI systems don’t just retrieve and reason but actually collaborate.
Today, most setups still rely on a single agent looping through planning, retrieval, and reasoning. In the near future, we’ll see multi-agent ecosystems emerge, networks of specialized agents that share memory, verify each other’s outputs, and coordinate toward complex goals.
Imagine a scenario inside a large enterprise:
- One agent focuses on retrieving content from internal documentation.
- Another agent analyzes that data and detects contradictions.
- A third acts by updating the knowledge base, generating a report, or triggering alerts.
- A fourth verifies the final result using a separate reasoning model or external API.
In practice, this means your analytics assistant could soon talk to your SEO agent, your CRM agent, and your reporting agent, each retrieving and reasoning within its own domain, then aligning on a shared answer.
These systems will evolve from passive copilots into distributed reasoning networks capable of handling uncertainty, breaking down complex workflows, and improving themselves through feedback.
For enterprises, the implications are enormous:
- Continuous monitoring and explanation of KPIs.
- Self-updating dashboards that learn what matters most.
- Internal knowledge graphs that stay synchronized across departments.
- Autonomous workflows that close the loop between insight and action.
It’s not science fiction. It’s the next logical evolution once retrieval, reasoning, and agency converge. A future where machines don’t just answer our questions, they help us ask better ones. So no, the future has not been written already…

This image was generated by AI.
Wrapping up
If classic RAG was the bridge between search and generation, Agentic RAG is the moment that bridge comes alive. It reasons, checks, and acts, helping to avoid hallucinations and turning information retrieval into an intelligent decision flow. That small difference changes everything: accuracy, trust, adaptability, and scale.
In enterprise settings, this means moving from static chatbots to dynamic intelligence systems that learn from their own actions. It means fewer hallucinations, faster context understanding, and insights that are actually grounded in truth. Agentic RAG doesn’t replace human expertise–it amplifies it. And that’s exactly what we build at Digital Loop.
We’ve developed custom Enterprise MarTech systems that unify data from marketing tools, including analytics, CRM, SEO platforms, ads, and more, into one consistent source of truth. From there, our AI layer lets us and our clients talk to data directly. We can ask questions, detect anomalies, or uncover new growth patterns through conversational AI interfaces powered by our own Talk-to-Data framework.
If you’re ready to see how Agentic RAG principles can supercharge your enterprise marketing ecosystem, let’s talk. Reach out to explore how our tailored MarTech solutions can help you turn complex data into actionable intelligence.